Kiunga biosphere reserve, designated in 1980, is in the north-eastern part of Kenya’s coastal strip. The ecosystem comprises of sandy beaches, sand dunes, scattered islands, shrublands, mangrove forests, coral reefs and sea-grass beds. These ecosystems within the biosphere reserve are critical in clean water provisions; and hosts diverse sea birds, turtles, and dugongs. Its coral reefs, sand dunes and beach offer opportunities for water sports and tourism. The local communities engage in fishing, forestry, agriculture, beekeeping, as well as manufacturing and construction-related activities. Kiunga Biosphere Reserve is part of the World Networks of Island and Coastal Biosphere Reserves.
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/kiunga
Amboseli Biosphere Reserve, located at the northern footsteps of Mount Kilimanjaro on the Kenyan border side, hosts a variety of ecological zones inclusive of natural dry mountain forest, mountains, savannah rangelands, saline plains, wetlands and fresh-water swamps. These areas are habitats to a wide variety of species like elephants, lions and giraffes. Designated in 1980, the predominant ecosystem reflects the mainly semi-arid environment. It is home to the Big 5 among other unique species like the African Sandalwood tree (Osyris lanceolate).
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/amboseli
Mount Elgon Transboundary Biosphere Reserve is a protected area located at the border between Kenya and Uganda. Mount Elgon, Kenya and Mount Elgon Uganda were then designated by UNESCO Man and Biosphere Reserves (MAB) Programme, as Biosphere Reserves in 2003 and 2005 respectively. It was designated as a Transboundary Biosphere Reserve in 2023. The biosphere reserve surrounds Mount Elgon, an extinct volcano. The biosphere reserve promotes conservation, sustainable development, and cooperation between the two nations in managing the shared natural resources and biodiversity in the region. Due to its diverse landscapes, Mount Elgon Forest Ecosystem hosts a variety of flora and fauna. Over 140 bird species have been recorded in the area. According to IUCN, the forest ecosystem also hosts 37 faunal species, which are “globally threatened” (22 mammal, 2 insect and 13 bird species, of which nine species are endemic). This makes the forest ecosystem a priority biodiversity hotspot vital for species conservation. The volcanic caves in Kenya are frequently visited by elephants which come to lick salt.
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/mount-elgon-kenya
Mount Kenya Biosphere Reserve was designated in Biosphere Reserve in 1978. The biosphere reserve is an iconic and ecologically diverse landscape that encompasses the iconic Mount Kenya, the highest mountain in Kenya. The Biosphere Reserve has a myriad of ecosystems, from lush afro-montane forests, moorlands to alpine moorlands. It hosts range-restricted flora such as the giant groundsel and giant lobelia; and endemic fauna species such the river frog, ide-stripped chameleon, the marine viper, king mole rat and the mole shrew. Mount Kenya National Park and adjacent forest reserves were inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1997.
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/mount-kenya-lewa
Mount Kulal Biosphere Reserve, designated in 1978, is a biodiversity hotspot located northern Kenya, and in the middle of one of the driest regions in East Africa. The landscape ranges from i) the mountain top habitat; ii) the flanks, gorges, and valleys; and iii) the surrounding flat lands all being niches to unique biodiversity. The mountainous ecosystem captures moisture in form of mist and rain thus provides important hydrological features for the entire northern Kenya. Lake Turkana to the west of Mt. Kulal harbors a great variety of aquatic fauna, including crocodiles, hippopotami, fish and birds. The biosphere reserve is an important bird area with approximately eighty-four (84) bird species having been recorded, including 34 Palearctic migrants and the endemic Kulal White-eye Zosterops kulalensis.
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/mount-kulal
The Malindi-Watamu-Arabuko-Sokoke Biosphere Reserve located approximately 100 kilometers north of Mombasa is a unique conservation area located in Kenya’s coastal region. Designated in 1979, the biosphere reserve hosts one of the largest remaining tracts of coastal dry forests in East Africa. The unique habitat which encompasses the Sokoke forest, sand dunes, woodlands, savannah, tidal mud flats, fringe mangrove forests, coral reefs and sea-grass beds is home to rich diversity of flora and fauna and is home to over 270 bird species recorded in the area. The reserve is also inhabited by elephants, buffaloes and other mammals. It also doubles as a major cetacean migration route in the Western Indian Ocean, which warrants good marine stewardship to ensure their safe passage. Major attractions are boat trips, water sports, deep-sea fishing and sustainable coral viewing.
More info: https://en.unesco.org/biosphere/africa/malindi-watamu
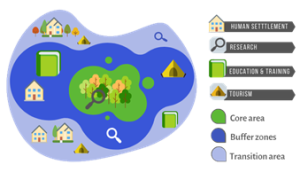 Biosphere reserves are globally designated and recognized areas by UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) programme. Biosphere Reserves (BR) are sites established by countries and recognized under UNESCO’s MAB programme to promote sustainable development based on local community efforts and scientific data. Biosphere reserves have three primary main roles:
Biosphere reserves are globally designated and recognized areas by UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) programme. Biosphere Reserves (BR) are sites established by countries and recognized under UNESCO’s MAB programme to promote sustainable development based on local community efforts and scientific data. Biosphere reserves have three primary main roles:
